WUMM-CM Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
In the CISNET Multiple Myeloma Incubator Program, the Washington University Modeling Group has constructed and calibrated a discrete-time, multi-state compartmental model of the natural history of multiple myeloma. This model follows birth cohorts of individuals as they progress from no disease to monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) to multiple myeloma (MM). The developed WUMM-CM model can be tailored to set research priorities and design clinical trials, including assessing sample sizes and power, evaluating the impact of treatment adherence of the participants, and determining the optimal treatment strategies. It can also be used to predict trial results and set policy goals.
Contact: Su-Hsin Chang, PhD, SM chang.su-hsin@wustl.edu
Overview
The WUMM-CM models the natural history of MM among birth cohorts. The model is a discrete time, multi-state compartmental model consisting of four compartments: Healthy (H), Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS), Multiple Myeloma (MM), and Death (D) (Fig. 1). Flow between compartments is governed by rates that depend upon age, gender, and race/ethnicity. Using a series of differential equations, the model deterministically calculates the proportion of each birth cohort that exists within each of the four compartments.
We calibrated our mathematical model to data on MGUS prevalence during 1999-2004 from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) and data on MM incidence during 2010 from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program. Data was stratified by age, gender, and race/ethnicity. Our calibrated model appropriately reproduced the patterns in the data (Fig. 2). The model was calibrated using a Bayesian statistical framework, so we estimate uncertainty in each model parameter.
In this model formulation, we assume that only age, gender, and race/ethnicity modulate the rates at which individuals flow through the compartments. No other covariates, including BMI, were considered in this version of the model. Smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) was not modeled as an intermediate state between MGUS and MM due to the lack of available data at the time of model development.
Outputs of our model include MGUS prevalence and incidence, MM incidence and prevalence, and the duration of pre-clinical dwell time (defined as the duration of time between MGUS development and MM development).
WUMM-CM
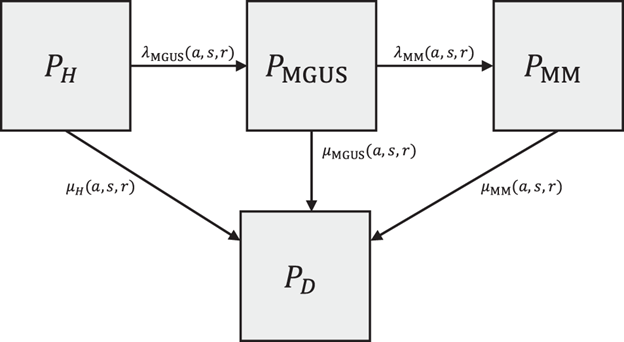
Figure 1: Model Schematic. Borrowed with permission from Huber et al. (2023).
Comparison to NHANES and SEER

Figure 2: Comparison of Fitted Model to NHANES and SEER Data. Reproduced with permission from Huber et al. (2023).
Reference
- Huber JH, Ji M, Shih YH, Wang M, Colditz G, Chang SH. Disentangling age, gender, and racial/ethnic disparities in multiple myeloma burden: a modeling study. Nat Commun 2023 Sep 20;14(1):5768.
Bladder models
- Kystis (Brown) Brown
- COBRAS (Ottawa) Ottawa
- SCOUT (NYU) NYU
Bladder Model Comparison Grid (PDF, 145 KB)
See all Comparison Grids & Profiles (Includes historical versions)
Lung models
- BCCRI-LunCan (BCCRI)
- BCCRI-Smoking (BCCRI)
- LCOS (Stanford)
- LCPM (MGH)
- MISCAN-Lung (Erasmus)
- SimSmoke (Georgetown)
- Smoking-Lung Cancer (Georgetown)
- MULU (Mount Sinai)
- ENGAGE (MDACC)
- YLCM (Yale)
- OncoSim-Lung (CPAC-StatCan)
- LMO (FHCC) (Historical)
Lung Model Comparison Grid (PDF, 161 KB)
See all Comparison Grids & Profiles (Includes historical versions)